Municipal water treatment
Magnetic media for water treatment / Denitrifying deep bed filter equipment / Improving BD Biochemical Tank Equipment / Low temperature belt type sludge drying machine / Magnetic media for water treatment / Automatic magnetic medium feeding machine

Products & Technology
Improving BD Biochemical Tank Equipment
Process Introduction
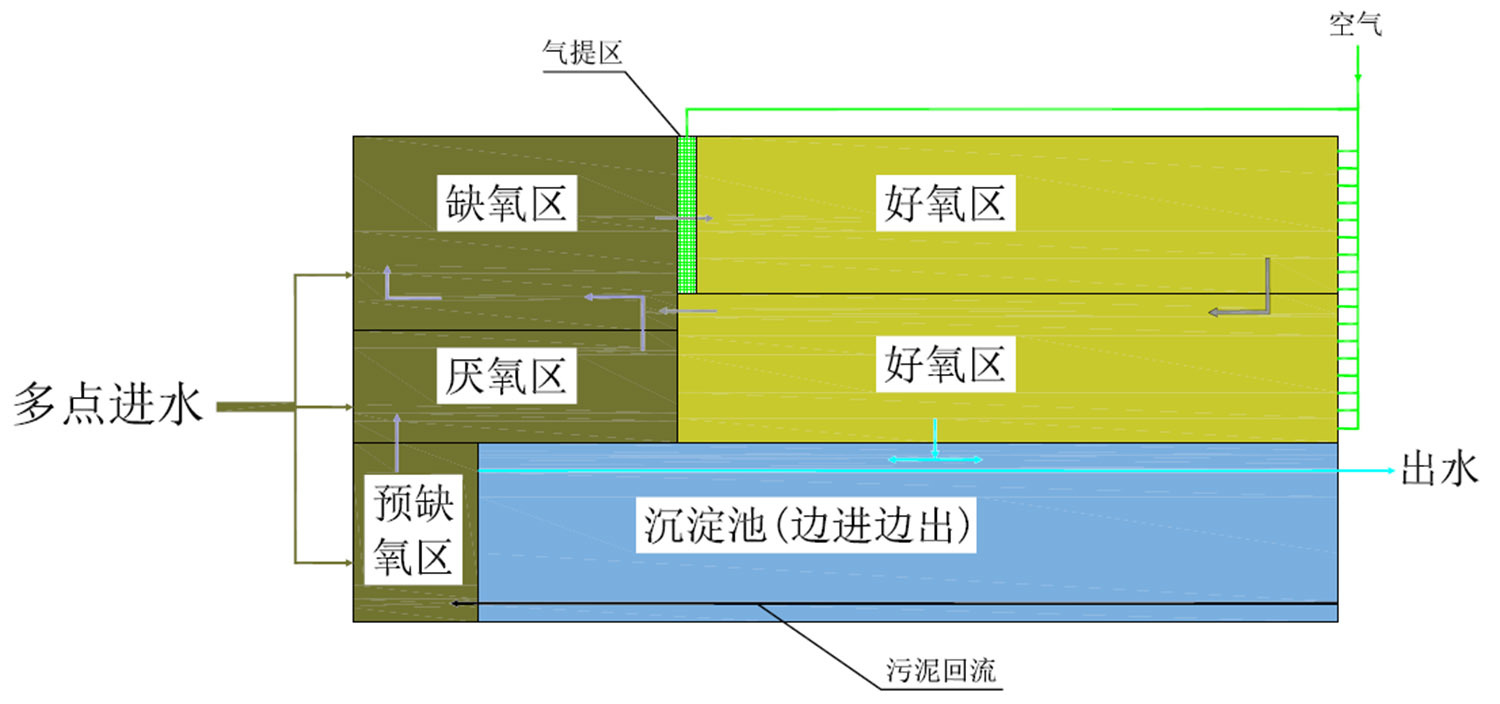
The improved BD biochemical tank is based on the traditional A2/O biochemical tank, which combines all single processes (biological nitrification, denitrification, phosphorus release, phosphorus absorption, organic matter oxidation, sedimentation, etc.) into a rectangular tank with several different treatment units adjacent to each other. Low dissolved oxygen (usually 0.3-0.5mg/L) is used to achieve vertical short-range nitrification/denitrification denitrification, High sludge concentration (usually 6-10g/L) ensures efficient and stable treatment.
The improved BD biochemical tank complete set of equipment can be manufactured into integrated equipment or implemented as a process package in water treatment engineering.
Technical characteristics
1. New and efficient aeration system: uniform gas distribution, high oxygen utilization rate, low energy consumption, able to replace aeration pipes online without stopping production, self-cleaning, and easy maintenance;
2. New gas lift reflux system: adopting a low head and large cross-section method to achieve high flow reflux, replacing the original reflux pump, low energy consumption, and reducing the maintenance volume of mechanical equipment;
3. High reflux ratio: can achieve a reflux rate of tens to hundreds of times, instantly dilute the influent concentration, and effectively resist influent impact loads;
4. Small footprint, simple structure, no external secondary sedimentation tank, saving sludge pump room and reflux pipeline, and saving investment;
5. Low operating costs: fewer mechanical equipment, low energy consumption, and less maintenance workload.
Applicable scope
1. New construction, renovation and expansion (upgrading and expanding) of municipal and industrial park sewage projects;
2. Industrial wastewater: petroleum, chemical, coal chemical, papermaking, printing and dyeing, pharmaceuticals, food, fermentation, electricity, garbage leachate;
3. Water environment management: river and basin management, point source interception, urban black and odorous water bodies;
4. Point source sewage treatment: townships, rural areas, high-speed service areas, villa areas, military camps.
Previous Page
Next Page
Previous Page
Next Page

